GitLab Version Check
What is the functionality of the GitLab Version Check?
GitLab Version Check is a suite of UI elements focused on communicating to instance admins the status of their current instance’s version. The status is communicated through various elements depending on how critical the version they are behind is.
GitLab Version Check UI Suite
GitLab Version Badge
Description
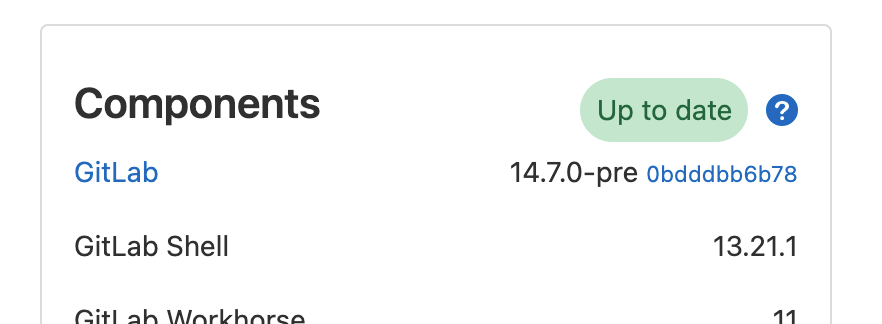
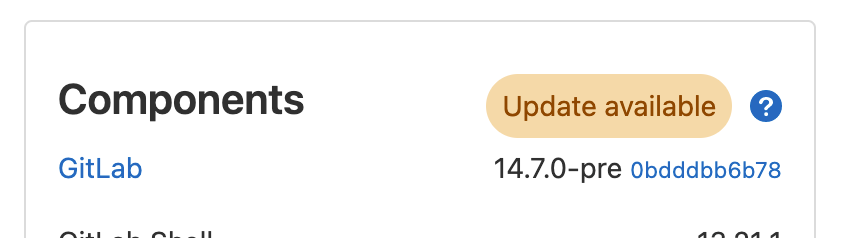
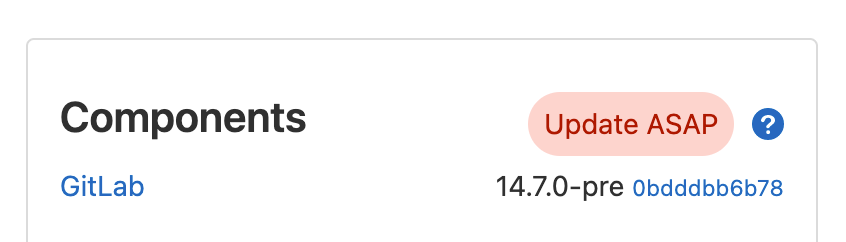
This badge element is always visible and communicates the GitLab instance version in relation to the upgrades available.
- Up to date: GitLab instance is fully up to date with the current version of GitLab.
- Update available: GitLab instance is outdated behind a non-security related version of GitLab.
- Update ASAP: GitLab instance is outdated behind a security related version of GitLab.
UI Representation
| Up to date | Update available | Update ASAP |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
UI Location(s)
- Admin Dashboard (Components Section)
- Help Page
- Help Dropdown (? icon in top navigation)
When to appear
- Always
GitLab Critical Security Upgrade Modal
Description
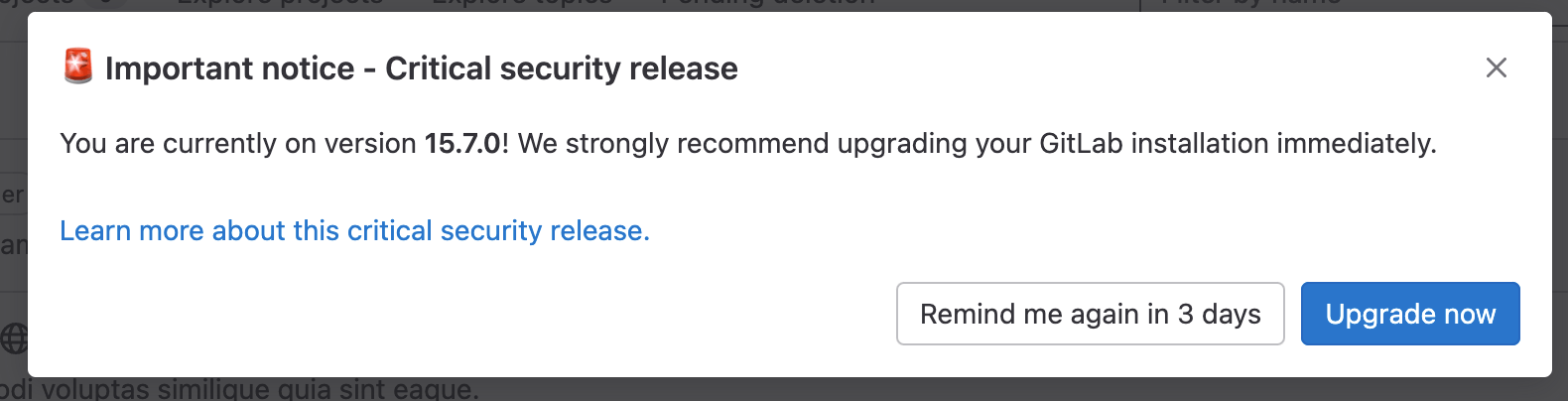
This Modal element is only visible when a GitLab instance is behind a security upgrade that could make the instance vulnerable. This modal appears and forces a interaction before going away. Depending on how verbose the upgrade notes are, the modal can appear with various levels of details. Additionally, when it appears, the admin is faced with a choice. Regardless of the choice made, the modal will be hidden and set to reappear in 3 days.
- Upgrade now: Admin is navigated to the upgrade documentation
- Remind me in 3 days: Modal is hidden
UI Representation
| No Stable Versions or Details | Stable Versions but no Details | Both Stable Versions and Details |
|---|---|---|
 |
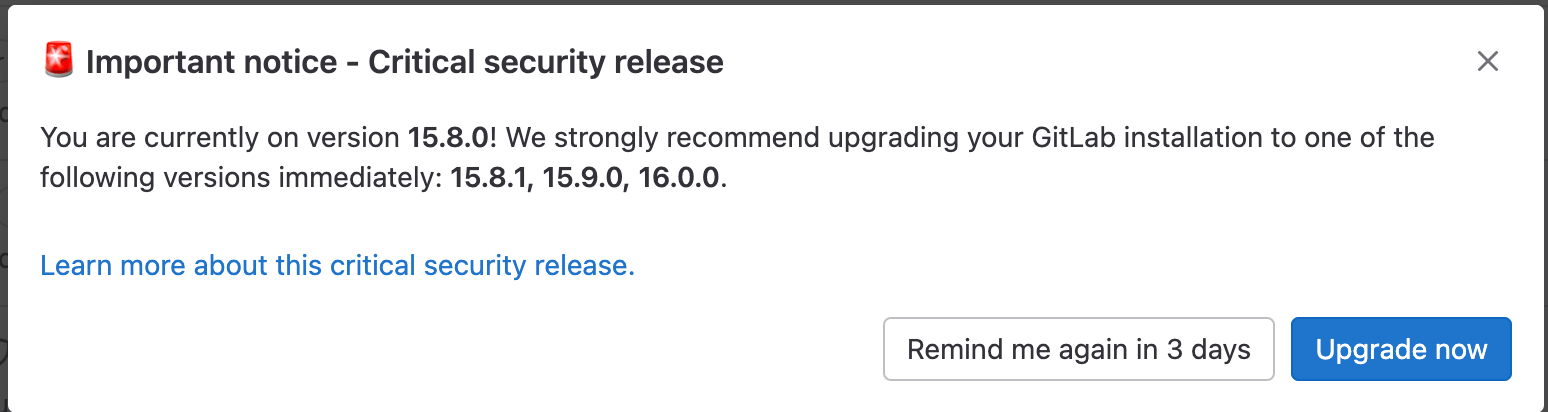 |
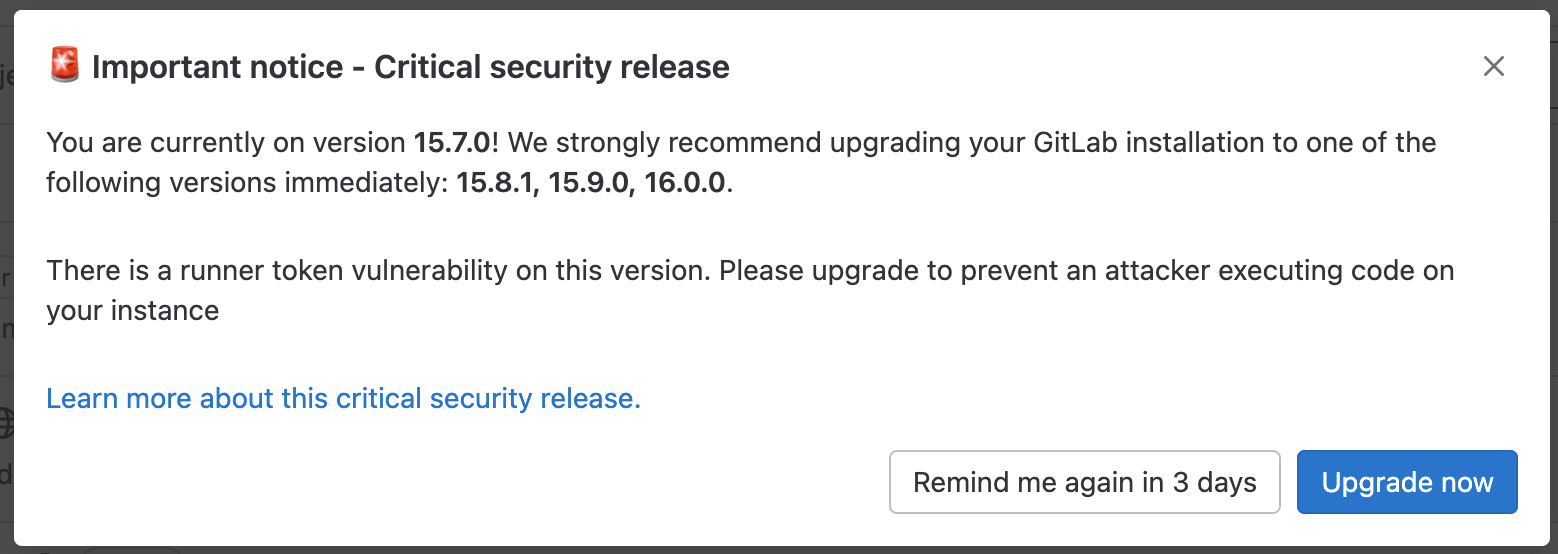 |
UI Location(s)
- Everywhere
When to appear
- If behind a
dangerlevel upgrade, always and dismissible for 3 day periods
How does the GitLab Version Check work?
In the past we used to provide the version check to the UI through an API call that you could see in your Network tab. This has changed and is now provided to the UI through Rails.
The current architecture is a bit complicated due to the nature of the ReactiveCaching mechanism we are using. This cache is powered by Sidekiq and is executed through Background Jobs (/admin/background_jobs) with the goal of housing and rehydrating your instance’s version status. We have an aggressive caching mechanism due to the nature of this data being fetched from an external endpoint and being needed throughout the GitLab application.
We have an exploration started into transitioning to Cron with a more traditional caching approach.
Below is a visual representation of how Version Check is managed behind the scenes:
graph TD
Z[Start] --> A
A[Version Request] --> B(Is Cached?)
B -->|Yes| C(Get Cache)
B -->|No| F[Schedule Immediate Sidekiq Job]
C --> |Data| A
C --> D(Reset 12hr Job Timer)
D --> E[Schedule 12hr Sidekiq Job]
E --> G
F --> G(Fetch Version from External API)
G --> H(Success?)
H --> |No| F
H --> |Yes| I(Write to Cache)
I --> D
Which information does the browser request contain?
The request contains information about the browser, the GitLab version and the HTTP referrer. The HTTP referrer is the URL from which the request was sent. So it is the URL of the help page or the admin area page of the admin’s GitLab instance. E.g. if you visit the help page on gitlab.com the HTTP referrer is https://gitlab.com/help. Furthermore the browser has to send the IP address of the instance combined with the request to receive a response. None of this information is saved.
What is version.gitlab.com?
Version.gitlab.com responds to the requests mentioned above with up-to-date version information. It does not save any of the provided data.
Which information can be derived from the HTTP referrer?
The HTTP referrer can contain the local or public hostname or IP address of a GitLab instance. It depends on how the admin accessed the GitLab web interface. Local hostnames and local IP addresses are only relevant and reachable within the local network in which the instance is running. Therefore local hostnames can be named anything, for example ‘myownGitLab’. Public hostnames or IP addresses can contain information about the owner of the host network. For example if the HTTP referrer contains ‘dev.gitlab.org’ it is assumable that this instance is owned by GitLab.
Troubleshooting
Use the internal API to check the cache
By hitting the /admin/version_check.json endpoint you can see if there is cached data and what is being provided to the UI through Rails.
If the response is null there are few steps you can take:
- Ensure your network is whitelisting/allowing an external API request to reach out to
version.gitlab.com. - Ensure there is a background job scheduled in Sidekiq and it isn’t stuck behind something.
Ensure Sidekiq jobs are in healthy state
By visiting /admin/background_jobs, you can look into what jobs are scheduled/running/pending on your instance.
The job you will be looking for is called external_service_reactive_caching.
If the internal API is returning null or the upgrade badge is missing:
- Ensure there is a job scheduled ASAP and determine how to unblock it from executing.
- If the job is scheduled far out, force it to execute because something may have mis-queued in Sidekiq.
How do I disable GitLab Version Check
GitLab Version Check can be disabled via the Metrics and Profiling tab of the GitLab Admin Settings.
You can find the checkbox labeled “Enable version check” at “/admin/application_settings/metrics_and_profiling” in the Usage Statistics section.
b6b4602f)
