Traditional cryptographic keys have created security issues and management overhead for software development teams for years. To address these security issues and ease the administrative burden, GitLab is partnering with Sigstore to use their command-line utility Cosign for keyless signing and verification, which can be done by adding just a few lines in a yml file.
Before digging too far into the integration, though, let's take a closer look at some of the issues of traditional key management and some of the benefits of keyless signing.
Traditional key management
Cryptographic keys have been a mainstay of securing software and network elements for years. Traditional key management involves the generation, storage, distribution, and protection of cryptographic keys that are essential for processes like encryption, decryption, and digital signing. While these methods have worked well over the years, they pose challenges that can impact security and operational efficiency.
-
Complexity and risk of exposure: Generating, storing, and distributing cryptographic keys manually can be error-prone and time-consuming. This complexity increases the risk of key exposure due to mismanagement or vulnerabilities in the key storage systems.
-
Security risk: Risk that the key management system (KMS) might be compromised and the private key leaked. There is no way for users to verify that the public key has not been tampered with or modified.
-
Key rotation complexity: Regular key rotation is a security best practice, but it can be complex to manage, especially when dealing with large numbers of keys. Key rotation will often disrupt applications.
-
Key revocation: Revoking access to keys that are no longer needed or that have been compromised can be challenging, especially if those keys are widely used across different parts of your application.
-
Integration complexity: Integrating your application with a KMS can introduce complexity. If your application is distributed or consists of microservices the complexity increases.
-
Key distribution: There is no standard way of distributing public keys. A system for distribution must be selected and secure, and if that system is compromised the public key must be changed.
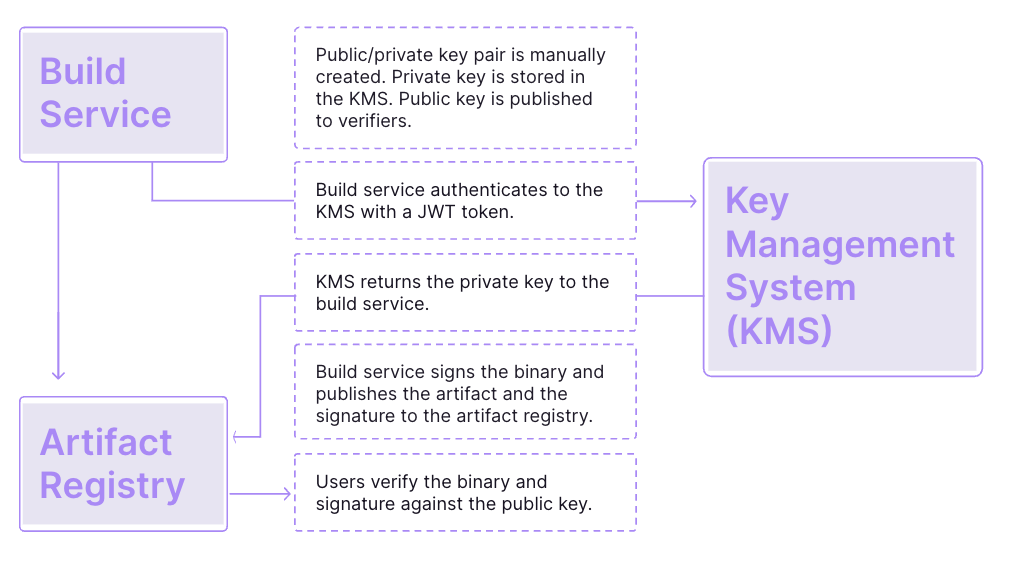
How traditional key management works
The move to keyless signing
Recently, the industry has been making a push towards keyless signing. With keyless signing, a message is signed using an ephemeral key that is generated and used for signing. The key is only valid for a few minutes, greatly reducing the complexity and security issues associated with traditional key management.
Keyless signing has several advantages.
-
Enhanced security: Keyless signing removes the need to store private keys on user devices, reducing the risk of exposure to malware or unauthorized access.
-
Simplified key management: With keyless signing, the complexities of key generation, distribution, and rotation are abstracted, leading to simplified key management processes. This streamlines operational workflows and reduces the potential for human error.
-
Audit trail: Keyless signing systems provide comprehensive audit trails and logging. Artifact verification is possible since public keys cannot be tampered with.
-
Remote signing and access: Keyless signing allows remote signing operations, enabling users to sign documents and transactions securely from anywhere. This capability enhances accessibility and collaboration without sacrificing security.
-
Regulatory compliance: The audit trails and accountability provided by keyless signing solutions facilitate regulatory compliance. With keyless signing, organizations can more confidently meet industry standards and demonstrate their commitment to secure practices.
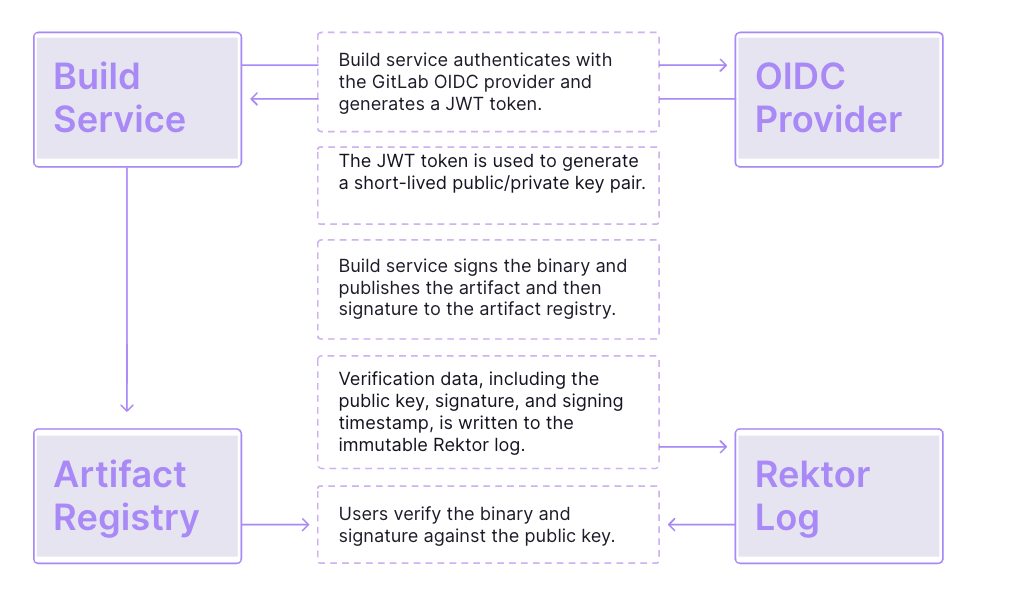
How keyless signing works
Keyless signing within GitLab
GitLab has partnered with one of the leaders in the keyless signing space, Sigstore, to help customers move away from traditional keys and easily make the transition to keyless signing.
The Sigstore project provides a command-line utility called Cosign, which can be used for keyless signing of container images built with the GitLab CI/CD. By adding a few lines of code to the GitLab yml file, GitLab users can use Cosign to leverage the benefits of keyless signing. Sigstore’s Cosign enables software developers to sign release files, binaries, and other software artifacts.
Once enabled within GitLab, when a user runs a pipeline, Cosign requests a short-lived key pair to use for signing, records it on a certificate transparency log (Rektor), and then discards it. The key is generated through a token obtained from the GitLab server using the OIDC identity of the user who ran the pipeline. This token includes unique claims that certify the token was generated by a CI/CD pipeline. The private key only lasts for a short time so there is no need to store it or rotate it. With Cosign, verification data, including the public key, signature, and signing timestamp, is written to the immutable Rektor log (an append-only transparency ledger) so that signing events can be publicly audited. Users can then verify the binary and signature against the public key.
The whole process is quick and easy and greatly increases system-wide security. With this integration, there is no longer a need to set up a key management system, no longer a need to rotate keys, and no longer a need to distribute public keys. Life is simpler and more secure!
Next steps
This feature is now available on all tiers of GitLab SaaS.
Watch a setup demo here:
For more details, check out Sigstore’s keyless signature documentation and then start your free trial of GitLab Ultimate.



