The GitLab Agent for Kubernetes (agentk) is an active in-cluster component for solving GitLab and Kubernetes integration tasks in a secure and cloud-native way. The agentk communicates to the GitLab Agent Server (KAS) to perform GitOps operations.
In many examples, we see the agent being deployed with global-level permissions on your Kubernetes cluster. There are use cases where we want to reduce the scope of what agentk has access to. In this guide I will provide information on deploying agentk on your cluster, limiting what namespaces it can access, as well as using it to deploy your applications.
Prefer a video? Watch the walkthrough below to learn how to deploy agentk to your cluster:
How it works
Anytime a developer performs changes to a manifest file managed within GitLab, the agentk will apply these changes to the Kubernetes cluster.
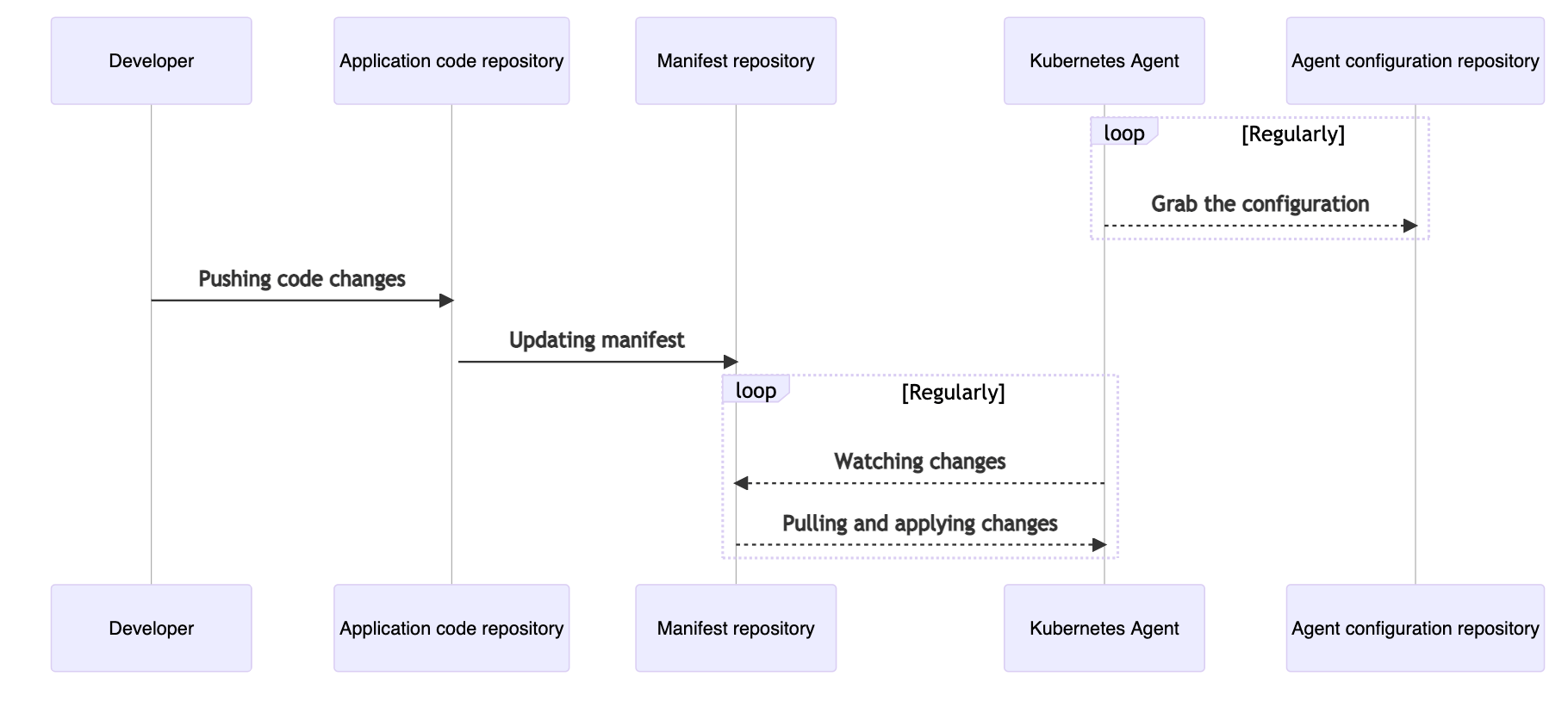 How a change to a manifest file in GitLab is applied to the Kubernetes cluster.
How a change to a manifest file in GitLab is applied to the Kubernetes cluster.
The agentk and the KAS use bidirectional streaming to allow the connection acceptor (the gRPC server, GitLab Agent Server) to act as a client. The connection acceptor sends requests as gRPC replies.
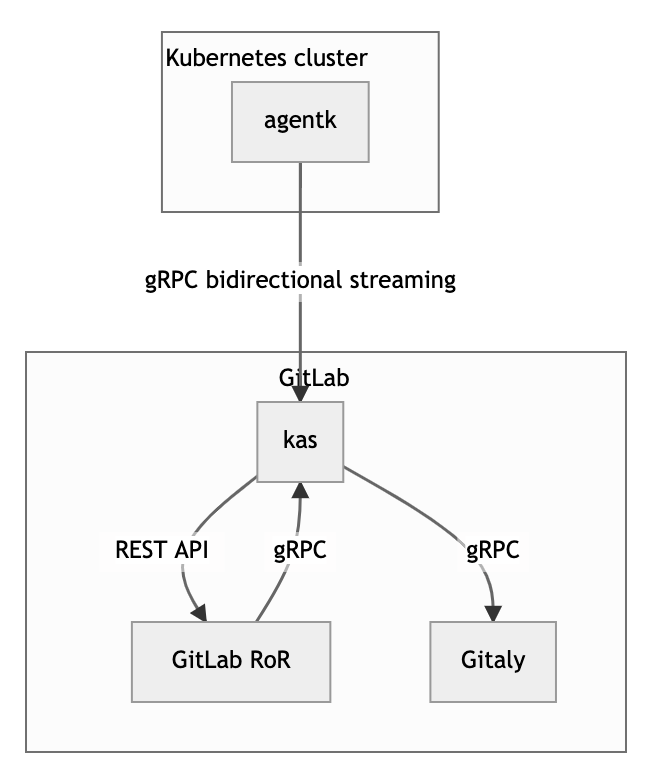 How bidirectional streaming with agentk works.
How bidirectional streaming with agentk works.
-
GitLab RoR is the main GitLab application. It uses gRPC to talk to kas.
-
agentkis the GitLab Agent for Kubernetes. It keeps a connection established to a kas instance, waiting for requests to process. It may also actively send information about things happening in the cluster. -
KAS is the GitLab Agent Server, and is responsible for:
- Accepting requests from agentk
- Authentication of requests from agentk by querying GitLab RoR
- Fetching the agent's configuration file from a corresponding Git repository by querying Gitaly
- Matching incoming requests from GitLab RoR with existing connections from the right agentk, forwarding requests to it, and forwarding responses back
- Polling manifest repositories for GitOps support by communicating with Gitaly
How to deploy the GitLab Agent
In order to deploy the agent, we require the following:
- Kubernetes cluster (I am using Google Kubernetes Engine, or GKE)
- The GitLab project which will hold the agentk configuration and deployment manifest, you can import Simple Agent K which includes an application and CICD configured
Note: The agentk configuration file and deployment manifests can be located in different projects. It just depends how you want to organize the GitOps workflow.
1. Create .gitlab/agent/agent-name/config.yaml directory in your project and replace agent-name with whatever you want to name your agent.
gitops:
manifest_projects:
- id: "Your Project ID"
paths:
- glob: '/manifests/*.{yaml,yml,json}'
Remember to replace Your Project ID with the projectID of your project, seen below:
 Fill in the projectID section with your information.
Fill in the projectID section with your information.
Note: You can also use the path to the project in GitLab, i.e., mygroup/mysub/myproject.
2. Create agent record in GitLab
A GitLab Rails Agent record is used to associate the cluster with the configuration repository project.
- Go to Infrastructure > Kubernetes tab
 Click the Kubernetes cluster tab in GitLab.
Click the Kubernetes cluster tab in GitLab.
- Click on the GitLab Agent managed clusters tab
 What the GitLab Agent tab looks like
What the GitLab Agent tab looks like
- Click the Install a new GitLab Agent button
 What the "Install new GitLab agent" button looks like.
What the "Install new GitLab agent" button looks like.
- Select your agent
 How to select your agent in GitLab
How to select your agent in GitLab
- Save the provided token
 Click here to save your provided token.
Click here to save your provided token.
3. Open a Terminal window
4. Scope kubectl to your cluster
$ gcloud container clusters get-credentials fern-gitops-2 --zone us-central1-c --project group-cs-9b54eb
Fetching cluster endpoint and auth data.
kubeconfig entry generated for fern-gitops-2.
5. Create the namespace for the Kubernetes agent
$ kubectl create ns gitlab-kubernetes-agent
namespace/gitlab-kubernetes-agent created
6. Create agent secret
This secret is used to store the token needed to configure the agent.
$ kubectl create secret generic -n gitlab-kubernetes-agent gitlab-kubernetes-agent-token --from-literal=token='YOUR_AGENT_TOKEN'
secret/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-token created
7. Apply the agentk deployment with limited access
In this deployment below, we will create the following:
Namespaces
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent: Where the agent will be deployed
- dude: A namespace where agentk has permission to deploy
- naww: A namespace where the agentk has no permissions
Service accounts
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent: Service account used for running agentk
Deployments
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent: The actual agentk client application
Cluster roles and bindings
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-cm: Permission for agentk to write all configmaps on the cluster
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-cm: Permission for agentk to read all configmaps on the cluster
Roles and bindings
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write: Permission for agentk to write all resources on gitlab-kubernetes-agent ns
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read: Permission for agentk to read all resources on gitlab-kubernetes-agent ns
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-dude: Permission for agentk to write all resources on dude ns
- gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-dude: Permission for agentk to read all resources on dude ns
The next step is to create the deployment file agentk.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: dude
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: naww
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
spec:
serviceAccountName: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
containers:
- name: agent
image: "registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/cluster-integration/gitlab-agent/agentk:stable"
args:
- --token-file=/config/token
- --kas-address
- wss://kas.gitlab.com # for GitLab.com users, use this KAS.
volumeMounts:
- name: token-volume
mountPath: /config
volumes:
- name: token-volume
secret:
secretName: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-token
strategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 0
maxUnavailable: 1
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-cm
rules:
- resources:
- 'configmaps'
apiGroups:
- ''
verbs:
- create
- update
- delete
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding-cm
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-cm
kind: ClusterRole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-cm
rules:
- resources:
- 'configmaps'
apiGroups:
- ''
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding-cm
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-cm
kind: ClusterRole
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write
rules:
- resources:
- '*'
apiGroups:
- '*'
verbs:
- create
- update
- delete
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write
kind: Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read
rules:
- resources:
- '*'
apiGroups:
- '*'
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read
kind: Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: dude
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-dude
rules:
- resources:
- '*'
apiGroups:
- '*'
verbs:
- create
- update
- delete
- patch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: dude
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding-dude
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-dude
kind: Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: dude
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-dude
rules:
- resources:
- '*'
apiGroups:
- '*'
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
namespace: dude
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding-dude
roleRef:
name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-dude
kind: Role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
subjects:
- name: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: gitlab-kubernetes-agent
Now we can apply the deployment with the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f k-agent.yaml
namespace/dude created
namespace/naww created
serviceaccount/gitlab-kubernetes-agent created
deployment.apps/gitlab-kubernetes-agent created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-cm created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding-cm created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-cm created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding-cm created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-dude created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-write-binding-dude created
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-dude created
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/gitlab-kubernetes-agent-read-binding-dude created
Note: You see we are giving permissions to the gitlab-kubernetes-agent on the dude namespace, but not on the naww namespace. Currently, permissions for ConfigMaps are necessary but the scope can be reduced.
8. Make sure agentk is running
$ kubectl get pods -n gitlab-kubernetes-agent
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gitlab-agent-58869d96bd-nqqnf 1/1 Running 0 10s
Now that the agentk is deployed, it can start managing our Kubernetes deployments.
Managing deployments
Now let's go back to the GitLab UI, and add some applications to deploy using GitOps.
1. Open the Web IDE and create a manifest folder in your project root
2. Add a manifest file for what you want to deploy on the dude namespace, name it dude.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment-dude
namespace: dude # Can be any namespace managed by you that the agent has access to.
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
3. Add a manifest file for what you want to deploy on the naww namespace and name it naww.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment-naww
namespace: naww # Can be any namespace managed by you that the agent has access to.
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
4. Commit changes and wait for the pipeline to run
5. Check dude namespace
$ kubectl get pods -n dude
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-deployment-dude-66b6c48dd5-rpxx2 1/1 Running 0 6m22s
Notice that the application has deployed.
6. Check naww namespace
$ kubectl get pods -n naww
No resources found in naww namespace.
Notice there is nothing on there.
7. Look at the k-agent logs
$ kubectl get pods -n gitlab-kubernetes-agent
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gitlab-agent-58869d96bd-nqqnf 1/1 Running 0 10s
$ kubectl logs gitlab-agent-58869d96bd-nqqnf -n gitlab-kubernetes-agent
{"level":"info","time":"2021-08-19T19:17:26.088Z","msg":"Feature status change","feature_name":"tunnel","feature_status":true}
{"level":"info","time":"2021-08-19T19:17:26.088Z","msg":"Observability endpoint is up","mod_name":"observability","net_network":"tcp","net_address":"[::]:8080"}
{"level":"info","time":"2021-08-19T19:17:26.375Z","msg":"Starting synchronization worker","mod_name":"gitops","project_id":"devsecops/gitops-project"}
...
You should see logs as follows:
Application successfully deployed to dude
{"level":"info","time":"2021-08-20T22:03:57.561Z","msg":"Synchronizing objects","mod_name":"gitops","project_id":"29010173","agent_id":711,"commit_id":"221499beaf2dcf267cd40324235570001e928817"}
{"eventType":"resourceStatus","group":"apps","kind":"Deployment","message":"Deployment is available. Replicas: 1","name":"nginx-deployment-dude","namespace":"dude","status":"Current","timestamp":"2021-08-20T22:03:58Z","type":"status"}
Application failed to deploy to naww
{"eventType":"resourceStatus","group":"apps","kind":"Deployment","message":"","name":"nginx-deployment-naww","namespace":"naww","status":"Unknown","timestamp":"2021-08-20T22:03:29Z","type":"status"}
{"level":"warn","time":"2021-08-20T22:03:30.015Z","msg":"Synchronization failed","mod_name":"gitops","project_id":"29010173","agent_id":711,"commit_id":"221499beaf2dcf267cd40324235570001e928817","error":"1 resources failed"}
We can see that deployments only happen on the dude namespace because that is all the k-agent has access to. You can add access to other namespaces by creating Roles and RoleBindings for each namespace like we did for the dude namespace.
Securing GitOps workflow on Kubernetes
Now you have seen how you can create a more restrictive GitOps workflow, allowing you to meet your security needs.
Thanks for reading! I hope this guide brings you one step forward into using and securing your GitOps workflow on Kubernetes. For more information see the GitLab Agent documentation.
Photo by seabass creatives on Unsplash




