In this blog post, I'll go over the different ways to ensure separation of duties and continuous compliance with the GitLab DevOps platform. But first, let's level-set on two key concepts:
Compliance means being in accordance with guidelines and specifications that have been defined either by your corporation or a regulatory agency. Compliance helps maintain corporate ethics, appropriate user policies, security standards, and much more for the safety of consumers.
Non-compliance may result in a bundle of legal fees and fines, so it is very important to maintain compliance. While maintaining compliance, DevOps teams must also ensure sustained development velocity, providing necessary simplicity, visibility, and control.
Separation of duties requires multiple actors to complete a task to increase protection from error as well as prevent malicious activity. Separation of duties ensures roles best-suited for the job are the only ones that can perform it. As an example, some of the following actors are observed, each with a specific purpose:
- a developer will be responsible for developing new features
- a compliance officer will be responsible for creating and enforcing the usage of a pipeline
- an appSec engineer will be responsible for approving merge requests with vulnerabilities
Considering the above roles, we can ensure that a developer cannot change a running pipeline. This is a task that can only be performed by a compliance officer, ensuring only compliant code can be pushed without approval.
An appsec engineer is responsible for reviewing and approving code with vulnerabilities, ensuring proper mitigation can be performed, and that nothing comes as a surprise in the future. In this scenario, developers can't merge code until compliance and security requirements are met.
Compliance pipelines
It is important for compliance teams to be confident that their controls and requirements are set up correctly, but also that they stay set up correctly. To obtain this confidence, compliance pipelines can be configured.
Compliance pipelines allow group owners to define a compliance pipeline in a separate repository that gets executed in place of the local projects gitlab-ci.yml file. These pipelines can be set up in a few simple steps:
1. Create a project containing the CI files you would like to run. Make sure that only the security team and/or administator has access to ensure separation of duties. I created the Compliance and Deploy project, which contains the yamls I wish to enforce.
2. Create a compliance framework label to identify that your project has certain compliance requirements and needs additional oversight. This label can be created in Settings > General > Compliance Frameworks under your top-level group.
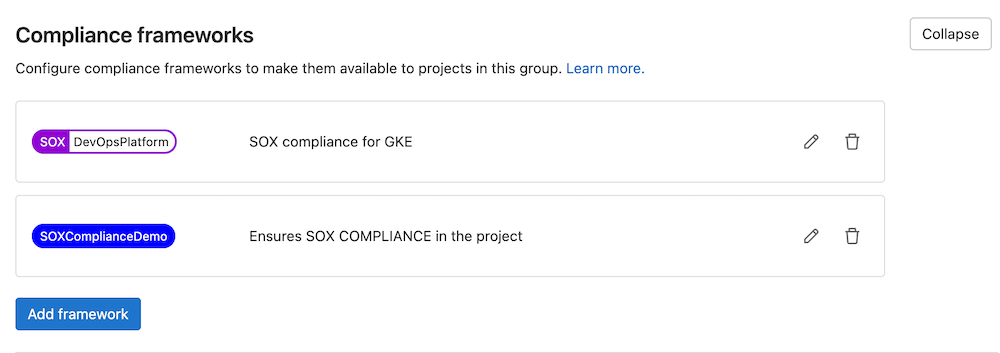
Note: Compliance labels can only be assigned to projects within the top-level group in which we create the label.
3. Within that framework, point to a compliance pipeline you wish to run, which is located in the project created in Step 1. Regardless of the CI file in a project, if the project is assigned a label, the defined pipeline will always run.

4. Assign the compliance label to a project within your top-level group. This can be done in Settings > General > Compliance Frameworks of the project on which you want to enforce compliance.
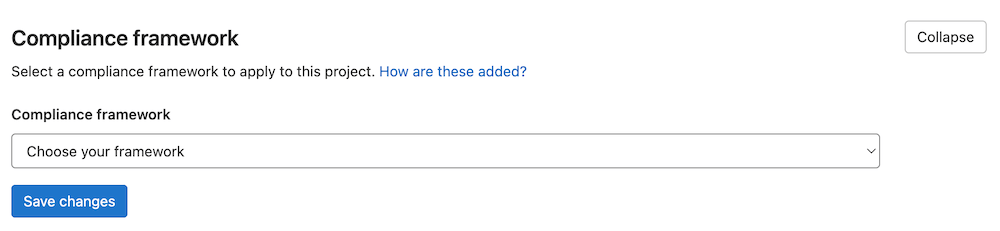
5. Run the pipeline
Now you can see that the pipeline is running the GitLab YAML from the Compliance and Deploy project. This can be seen in my Hypnotherapy Services project.
Security policies
GitLab provides Security Policies, which enable security teams to require security scans to run according to a configuration. This provides the security teams with confidence that the configured scans have not been changed or disabled.
There are two types of policies, Scan Execuition Policies and Scan Result Policies.
- Scan Execution Policies: Require that security scans run on a specified schedule or with the project pipeline
- Scan Result Policies: Take action based on scan results, such as requiring approval from the security team before a merge can occur
To take a quick view of the feature, see my explanation in the GitLab 14.8 Security Features video. These policies can be configured via the Policy Editor in a few simple steps:
Scan execution
1. Go to Security & Compliance > Policies
2. Create a new policy by pressing the New Policy button
3. Select Scan Execution
4. Create the rule. I'm creating a rule that requires SAST to be configured in order for a pipeline to run.
name: force_sast
description: 'require sast to run'
enabled: true
rules:
- type: pipeline
branches:
- main
actions:
- scan: sast
5. Submit the policy by creating a merge request and then merge
All scan execution policy changes are applied through a background job that runs once every 10 minutes. Allow up to 10 minutes for any policy changes committed to this project to take effect.
6. Try and run a pipeline. It will not be run unless SAST is defined in the YAML.
Note: You can also force SAST to run on a timer. For more information, see the scan execution policies documentation.
Scan result
1. Go to Security & Compliance > Policies
2. Create a new policy by pressing the New Policy button
3. Select Scan Result
4. Create the rule
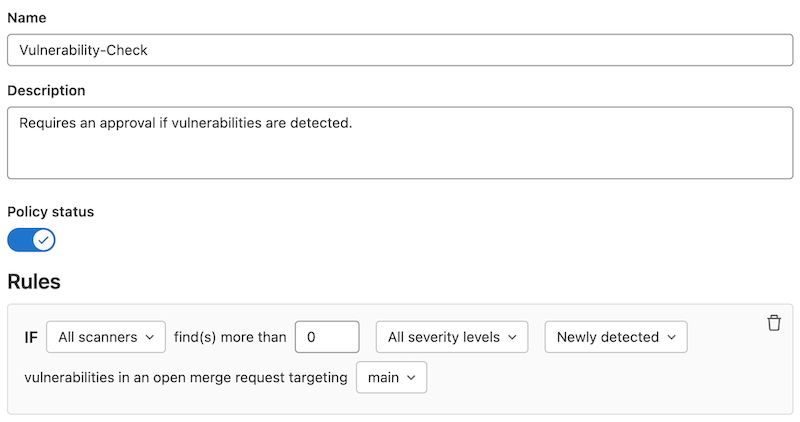
5. Add action to take
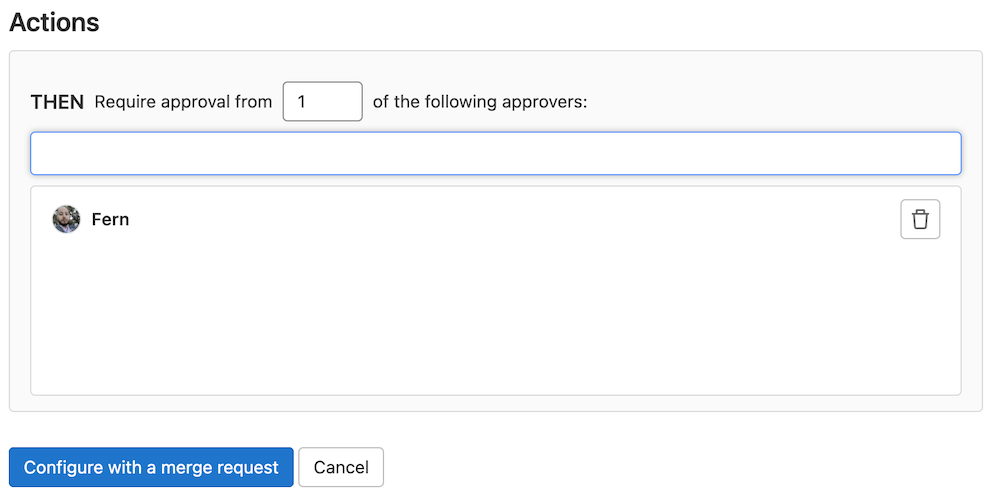
6. Submit the policy by creating a merge request and then merging
7. Create a separate merge request with vulnerabilities
You can see how to add vulnerabilities by checking out the Developer Workflow section of the GitLab DevSecOps Workshop.
8. Verify Scan Execution Policy is being used by viewing merge request
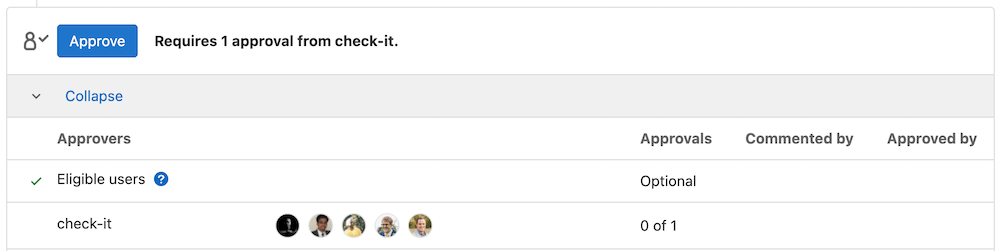
Audit Management and Compliance Dashbaord
Another important part of compliance is knowing it is actually happening in your groups/projects. GitLab has Audit Events and Compliance Reports to assist with audits.
Audit Events allows GitLab owners and administrators to track important events such as who performed certain actions and the time they occurred.
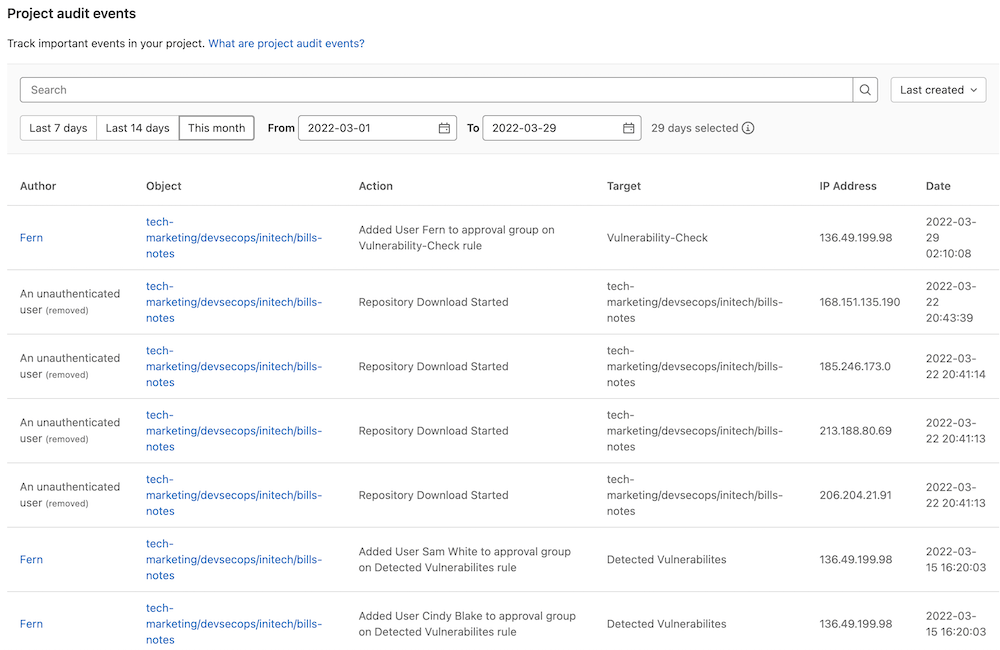
Audit Events records different events per group and per project, which can be seen in the audit events documentation. Audit Events can be accessed by going to Security & Compliance > Audit Events Some examples include:
- user was added to project and their permissions
- permission changes of a user assigned to a project
- project CI/CD variable added, removed, or protected status changed
- user was added to group and their permissions
- group name or path changed
Audit Events can also be sent to an HTTP endpoint using Audit Event Streaming. I show how to implement Audit Event Streaming in this video.
Compliance Report gives you the ability to see a group's merge request activity. It provides a high-level view for all projects in the group.
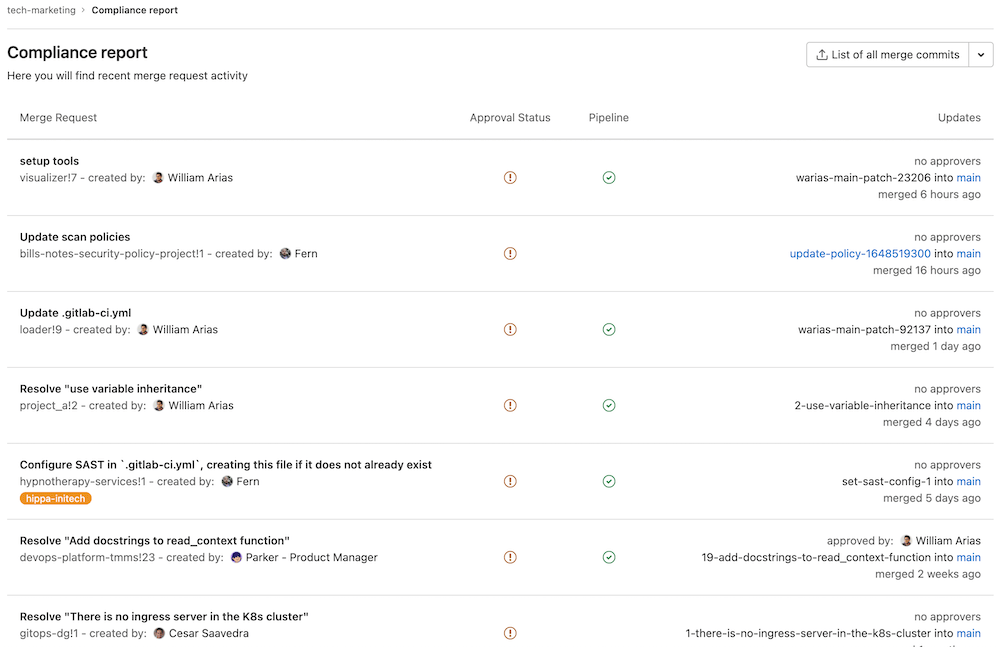
You can use the report to:
- get an overview of the latest merge request for each project
- see if merge requests were approved and by whom
- see merge request authors
- see the latest CI/CD pipeline result for each merge request
The Compliance Report can be accessed in the top-level group by going to Security & Compliance > Compliance Report.
Thanks for reading! For more information on separation of duties within GitLab, check out Continous Software Compliance with GitLab
Cover image by Maarten van den Heuvel on Unsplash




