As a single, all-inclusive platform, managing your DevSecOps lifecycle with GitLab is easy. GitLab’s platform enables developers to build better software faster. But the effectiveness of GitLab extends beyond DevSecOps.
In October of 2022, the International Organization for Standardization released the latest edition of the ISO 27001 standard. ISO/IEC 27001:2022 includes several changes from its previous edition, including the addition of Annex A controls focused on secure coding and configuration management.
At GitLab, we leverage our platform to support many aspects of our security compliance program, a concept we internally call dogfooding. An overview of the compliance and assurance credentials that we maintain can be found on our Trust Center page.
Let’s review the primary functions you can leverage to support your ISO 27001 compliance journey.
Organizational controls
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 5.3 Segregation of duties | Conflicting duties and conflicting areas of responsibility shall be segregated. |
| 5.15 Access control | Rules to control physical and logical access to information and other associated assets shall be established and implemented based on business and information security requirements. |
| 5.16 Identity management | The full lifecycle of identities shall be managed. |
| 8.2 Privileged access rights | The allocation and use of privileged access rights shall be restricted and managed. |
| 8.4 Access to source code | Read and write access to source code, development tools, and software libraries shall be appropriately managed. |
With GitLab, you can assign users a role when you add them to a project or group. A user’s role determines the actions they can take within your GitLab instance. The following roles are available for assignment:
- Guest (private and internal projects only)
- Reporter
- Developer
- Maintainer
- Owner
- Minimal access (available for the top-level group only)
GitLab’s roles enable you to limit a user’s permissions in accordance with the principle of least privilege and your business and information security requirements.
GitLab enables you to centralize authentication and authorization responsibilities for your GitLab instance through SAML SSO integrations. GitLab integrates with a wide range of identity providers to support our customers’ diverse tech stacks. GitLab also supports the System for Cross-Domain Identity Management (SCIM). Through GitLab’s SSO and SCIM integrations, you can automate the lifecycle of your user identities in a secure and efficient manner.
SSO and SCIM are also available for GitLab self-managed customers.
Note: Annex A Technological controls 8.2 and 8.4 were included in the chart above due to their close relationship with Organizational controls 5.3, 5.15, and 5.16. The same GitLab features can be applied to support these control requirements.
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 5.8 Information security in project management | Information security shall be integrated into project management. |
With GitLab, you can use our planning tools to support your project management efforts and ensure information security is being appropriately considered through all phases of a project’s lifecycle.
-
GitLab’s team planning features enable users to organize, plan, align, and track project work from idea to production.
-
Epics, issues, and tasks can be used to collaborate on ideas, solve problems, and plan work with your information security team. Description templates and checklists enable users to apply a consistent description and workflow to issues or merge requests. These templates support a consistent approach to integrating information security into your project management lifecycle.
-
Labels allow users to organize issues as they see fit. To support information security, labels may be used to identify the risk level associated with a project, identify the stage a project is in, or identify the information security team that is responsible for a set of work. Scoped labels can be used to add further logic to workflows by preventing certain labels from being used together. At GitLab, we leverage scoped labels to identify work assigned to different teams, the project stage the work resides in, and the product or feature set associated with the work.
Scoped Labels
- Group and project issue boards can be used to further organize your work and provide a central, aggregated view of all work associated with a group or project.
Technological controls
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 8.8 Management of technical vulnerabilities | Information about technical vulnerabilities of information systems in use shall be obtained, the organization’s exposure to such vulnerabilities shall be evaluated and appropriate measures shall be taken. |
| 8.9 Configuration management | Configurations, including security configurations, of hardware, software, services and networks shall be established, documented, implemented, monitored, and reviewed. |
| 8.25 Secure development lifecycle | Rules for the secure development of software and systems shall be established and applied. |
| 8.26 Application security requirements | Information security requirements shall be identified, specified, and approved when developing or acquiring applications. |
| 8.27 Secure system architecture and engineering principles | Principles for engineering secure systems shall be established, documented, maintained, and applied to any information system development activities |
With GitLab, you can store your hardware and software configurations, maintain version control, update your configurations via merge requests, and leverage GitLab’s CI/CD pipelines to push those configurations to your applications and infrastructure. GitLab enables organizations to implement GitOps through a single platform.
GitLab’s infrastructure-as-code scanning functionality enables you to scan your IaC configuration files for known vulnerabilities. GitLab’s IaC scanning supports a variety of IaC configuration files and languages making it adaptable to different tech stacks.
For compliance professionals, GitLab enables you to implement automation through compliance frameworks and compliance pipelines. These features enable users to identify critical projects that have certain compliance requirements and push configurations to those projects via pipelines. They enable consistent enforcement of controls, thereby supporting your security posture and facilitating adherence to your organization’s internal and external compliance requirements.
For Ultimate customers, GitLab’s Compliance Center provides a centralized view of a group’s compliance posture, such as the different compliance frameworks being applied to the projects in the group. You can even see how well you comply with the GitLab Standard.
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 8.15 Logging | Logs that record activities, exceptions, faults and other relevant events shall be produced, stored, protected, and analyzed. |
| 8.16 Monitoring activities Control | Networks, systems, and applications shall be monitored for anomalous behavior and appropriate actions taken to evaluate potential information security incidents. |
With GitLab, you can use audit events to track important events, including who performed the related action and when. Audit events cover a broad range of categories, including:
- Group management
- Authentication and authorization
- User management
- Compliance and security
- CI/CD
- GitLab Runners
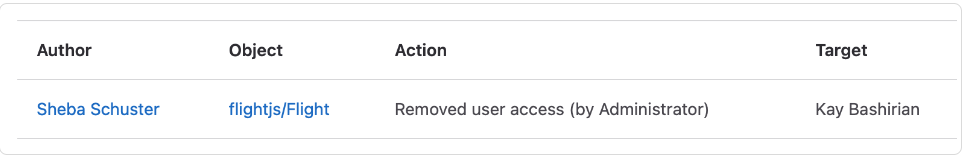
Example of an audit event
For Ultimate customers, audit event streaming can be enabled. Audit event streaming enables users to set a streaming destination for a top-level group or instance to receive all audit events about the group, subgroups, and projects, as structured JSON.
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 8.28 Secure coding | Secure coding principles shall be applied to software development. |
| 8.29 Security testing in development and acceptance | Security testing processes shall be defined and implemented in the development lifecycle. |
You can use the features in GitLab’s Secure stage to enhance your software development lifecycle and improve the security of your products. GitLab’s Secure stage features include:
- Static application security testing (SAST)
- Dynamic application security testing (DAST)
- Code quality
- Container scanning
- Dependency scanning
And much more!
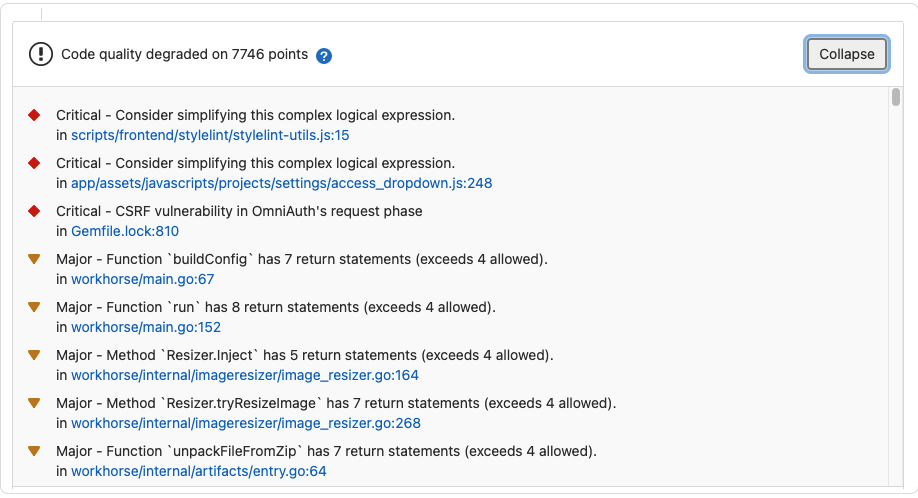
Code quality findings
Leaked secrets is one of the leading catalysts of security breaches. GitLab’s Secret Detection scans your repository to help prevent your secrets from being exposed.
GitLab’s Policies feature enables users to implement scan execution and scan result policies based on configured logic. These policies combine the scanning capabilities in the Secure stage with merge request approvals to further enforce compliance requirements.
Together, GitLab’s Secure features create a foundation for a secure software development lifecycle program and enable you to implement secure coding principles in accordance with your organization’s requirements.
| Control ID | Control Description |
|---|---|
| 8.32 Change management | Changes to information processing facilities and information systems shall be subject to change management procedures. |
GitLab offers many features to support a comprehensive change management program.
GitLab’s source code management features enable users to implement protected branches. Protected branches allow GitLab users to impose restrictions on certain branches that are considered critical to their operations. A protected branch controls:
- which users can merge into the branch
- which users can push to the branch
- if users can force push to the branch
- if changes to files listed in the CODEOWNERS file can be pushed directly to the branch
- which users can unprotect the branch
The default branch in a repository is automatically designated as a protected branch.
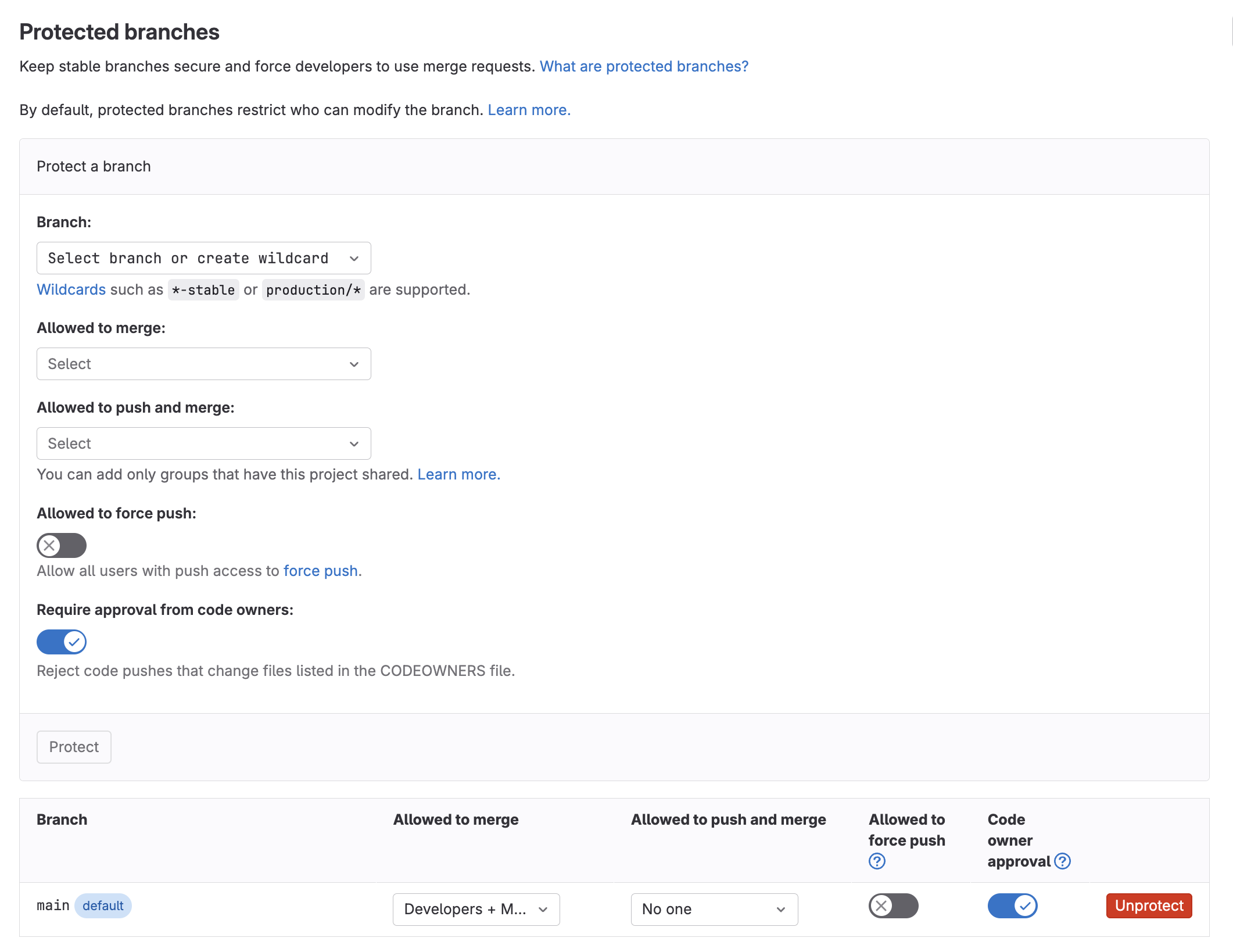
Protected branches settings within GitLab
Merge requests (MR) are a core component of the software development lifecycle. GitLab users can configure their MRs so that they must be approved before they can be merged. MR approvals allow users to set the minimum number of required approvals before work can merge into a project. Some examples of rules you can create include:
- Users with specific permissions can always approve work.
- Code owners can approve work for files they own.
- Users with specific permissions can approve work, even if they don’t have merge rights to the repository.
- Users with specific permissions can be allowed or denied the ability to override approval rules on a specific merge request.
As previously mentioned, issues and tasks can be used to document and collaborate on change requests. Description templates enable users to apply a consistent description to issues or MRs. These templates support a consistent approach to requesting changes in a manner that best fits your organization.
Learn more
As a comprehensive DevSecOps platform, GitLab supports a broad range of requirements. ISO added additional controls around secure coding and configuration management in the 2022 edition of the ISO standard. This demonstrates that certifying bodies have an increased focus on software security as a whole. As a strategic partner, GitLab can help support your ISO 27001 compliance journey and help you develop better software faster.
To learn more about these features, see our library of tutorials.



