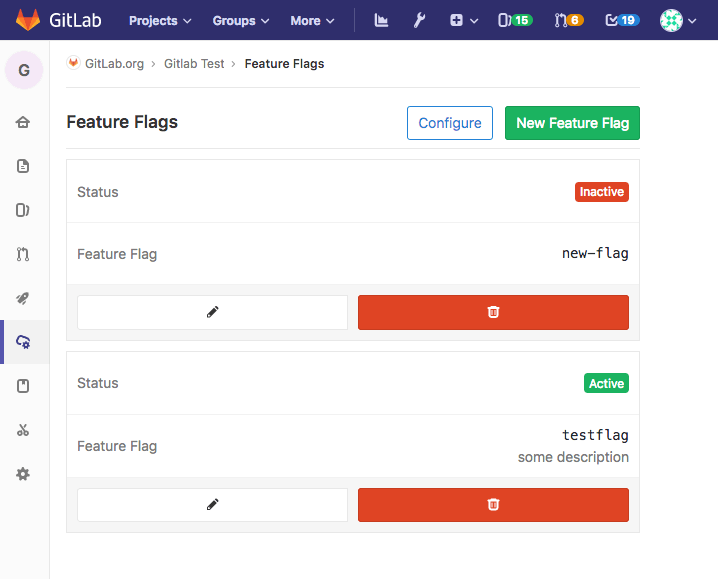
Create and toggle feature flags for your applications (alpha)
Create and toggle feature flags for your applications (alpha)
This feature gives you the ability to create and manage feature flags for your software directly in the product. Simply create a new feature flag, validate it using the simple API instructions in your software, and you have the ability to control the behavior of your software in the field via the feature flag within GitLab itself.
Feature Flags offer a feature toggle system for your application. They enable teams to achieve Continuous Delivery by deploying new features to production in smaller batches for controlled testing, separating feature delivery from customer launch. This helps reduce risk, and allows you to easily manage which features to enable.
Note that this is an alpha feature being introduced for the first time, so while we encourage you to check out the feature and provide feedback, we want you to be aware that the implementation could change in subsequent releases.
File tree for browsing merge request diff
File tree for browsing merge request diff
Code review is an essential practice of every successful project, but knowing what has changed can be hard to determine from a flat list of diffs. GitLab now includes a searchable file tree of changes to make it easy to see which files have changed and jump between them.
The file tree summarizes the structure and size of the change, similar
to diff-stats, providing an overview of the change and improving
navigation between diffs. Search allows reviewers to limit their code
review to a subset of files by path or filetype, simplifying reviews by
specialists focussed on only a subset of the merge request.
Previously the list of changed files was available through a searchable drop down, that was best suited to jumping to a specific file.

Suggest Code Owners as merge request approvers
Suggest Code Owners as merge request approvers
Knowing who is the best person to review your changes isn’t always obvious. Code owners are now shown as suggested approvers when creating or editing a merge request to make assigning the right person easy.
Support for defining code owners was introduced in GitLab 11.3. In upcoming releases, code owners will be further integrated into the merge request workflow with automatic assignment and required approvals.

New user profile page overview
New user profile page overview
No matter how engaged you are on GitLab, your activity is a relevant source of information and engagement indicator, displayed right at your personal profile page. Your personal profile should give a simple insight into what you are interested in and working on.
With this release, we introduce a redesigned profile page overview, showing your activity via the familiar but shortened contribution graph with your latest activities and your most relevant personal GitLab projects.

Set and show your status message within the user menu
Set and show your status message within the user menu
With GitLab 11.2 we introduced personal status messages for the first time, allowing you to share your current availability, mood, or simply your favorite animal.
With this release, we make setting your status even more simple and frictionless. A new “Set status” item in your user menu provides a fresh modal that allows you to set and clear your status right within context. In addition, your set status is also shown in your user menu, on top of your full name and user name, including set Emoji and message.

Move ability to use includes in .gitlab-ci.yml from Starter to Core
.gitlab-ci.yml from Starter to CoreMove ability to use includes in .gitlab-ci.yml from Starter to Core
We are very happy to announce in this release that the usage of
includes within the .gitlab-ci.yml is now available in Core. This
will help ensure templates and other shared resources are always
compatible between free and non-free users, and also unlocks the
ability for everyone to do best-practice development using reusable
snippets in your CI/CD pipelines.

Run jobs only/except for modifications on a path or file
only/except for modifications on a path or fileRun jobs only/except for modifications on a path or file
A popularly requested feature, we’re proud to now offer the
ability within the .gitlab-ci.yml to use only/except rules for jobs
based on when modifications occur to a specific file or path (glob).
This will allow more control for users whose repositories contain different kinds of assets or builds, ensuring only the appropriate steps are executed for the kinds of changes that were committed, speeding up overall pipeline execution.
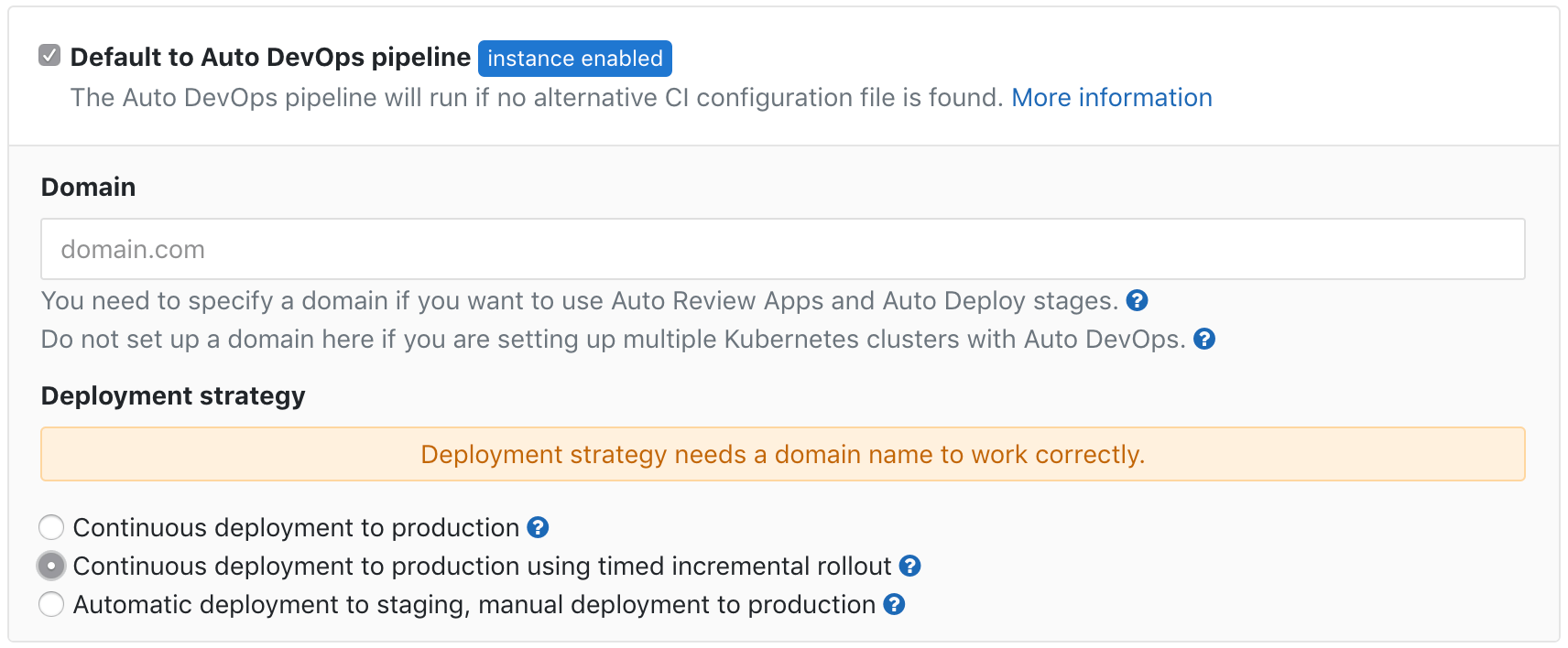
Add timed incremental rollouts to Auto DevOps
Add timed incremental rollouts to Auto DevOps
You’ve had the ability within Auto DevOps to setup incremental rollouts for a while now, and with this release, we are adding an option to also set up timed incremental rollouts where the rollout will automatically continue on a timed cadence unless there is some error.
Support Kubernetes RBAC for GitLab managed apps
Support Kubernetes RBAC for GitLab managed apps
Security is paramount when setting up your infrastructure for the first time or connecting to existing one. Role-based access control (RBAC) was made generally available as part of Kubernetes’ 1.8 release, providing more granular controls to regulate access to Kubernetes resources.
Our Kubernetes integration will now offer the capability to either create an RBAC-enabled cluster on GKE or to connect with an existing cluster that is RBAC-enabled, providing increased security for your infrastructure.

Auto DevOps support for RBAC
Auto DevOps support for RBAC
Auto DevOps now supports interacting with and deploying applications to RBAC-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
Role-based access control (RBAC) is an important tool that allows operators to ensure the reliability, security, and efficiency of their Kubernetes cluster. Using Auto DevOps in conjunction with an RBAC-enabled cluster ensures your applications take advantage of the increased infrastructure security.

Support PostgreSQL DB migration and initialization for Auto DevOps
Support PostgreSQL DB migration and initialization for Auto DevOps
Using Auto DevOps to automatically detect, build, test, deploy, and monitor your application just got more powerful. Starting in 11.4, Auto DevOps now provides the ability to initialize or migrate PostgreSQL databases in your project.
Simply define a project variable to initialize or migrate your PostgreSQL database, and Auto DevOps will do the rest.






















We want to hear from you
Enjoyed reading this blog post or have questions or feedback? Share your thoughts by creating a new topic in the GitLab community forum.
Share your feedback