Published on: March 15, 2023
6 min read
Getting started with GitLab application security
This tutorial shows how to incorporate GitLab security scan templates into a .gitlab-ci.yml file and view scan results.

As software security becomes increasingly important, many companies want to introduce standard code scanning processes into development workflows to find and remediate security vulnerabilities before they get to production.
GitLab's DevSecOps Platform allows users to perform security scans in CI/CD pipelines, which can easily be enabled to check applications for security vulnerabilities such as unauthorized access, data leaks, and denial of service (DoS) attacks.
While most of what is covered in this blog will pertain to Ultimate features, there are some features available for free and Premium tier users as well. By the end of this blog, you will have a solid starting point for adopting GitLab security scans, with any tier license, and understand the steps to take next to mature your DevSecOps practices.
Prerequisites
To enable security scanning for a project, you must have the following:
- a GitLab project that meets the requirements of the security scan you choose to enable, with CI enabled
- a
.gitlab-ci.ymlfile for the project that has at least a build job defined - a Linux-based GitLab Runner with the Docker or Kubernetes executor
Get started: Add a scan template to your pipeline
Here are the first steps to introduce security scanning.
Available security scans
GitLab provides a variety of security scanners, each with its own set of criteria for adoption:
| Scan type | Minimum tier | Prerequisites | Application requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static application security testing (SAST) | Free | None | See SAST requirements |
| Secret detection | Free | None | None |
| Container scanning | Free | Container image built and pushed to registry | Docker 18.09.03 or higher installed on the same computer as the runner; image uses a supported distribution |
| Infrastructure as code (IaC) scanning | Free | None | See supported languages and frameworks |
| Dependency scanning - includes license compliance | Ultimate | None | Application must use one of the supported languages and package managers |
| Dynamic application security testing (DAST) | Ultimate | Deployed target application | See GitLab DAST scanning options |
| Coverage-guided fuzz testing | Ultimate | Instrumented version of application | See supported fuzzing engines and languages |
| Web API fuzz testing | Ultimate | Deployed target application | See supported API types |
Many customers will start with secret detection, dependency scanning, or
SAST scanning, as they have the fewest requirements for usage.
Add the scanner template
GitLab provides a CI template for each security scan
that can be added to your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file. This can be done by manually editing the CI file and adding the appropriate template path in the templates section of the file. Several scanners can also be enabled via the UI, where a merge request will be created to add the appropriate scanner to the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
I will use a simple spring boot application as an example and enable dependency scanning, a scanner that is popular amongst our customers, as my first security scan. Dependency scanning will find vulnerabilities in the libraries I am using to build my application. My project is a Java application built via Maven and includes a pom.xml file, so it meets the requirements for dependency scanning. Since dependency scanning can be enabled via the UI, I'm going to take advantage of that feature here.
For this project, I have created a .gitlab-ci.yml file that contains a build and test stage and a build job. I'm using the Auto DevOps auto-build job, but you can define your own build job if desired. This is the starting pipeline code in my .gitlab-ci.yml file:
image: alpine:latest
include:
- template: Jobs/Build.gitlab-ci.yml # https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab-foss/blob/master/lib/gitlab/ci/templates/Jobs/Build.gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- build
- test
To enable dependency scanning, I'll first navigate to the Security & Compliance menu, Configuration sub-menu.
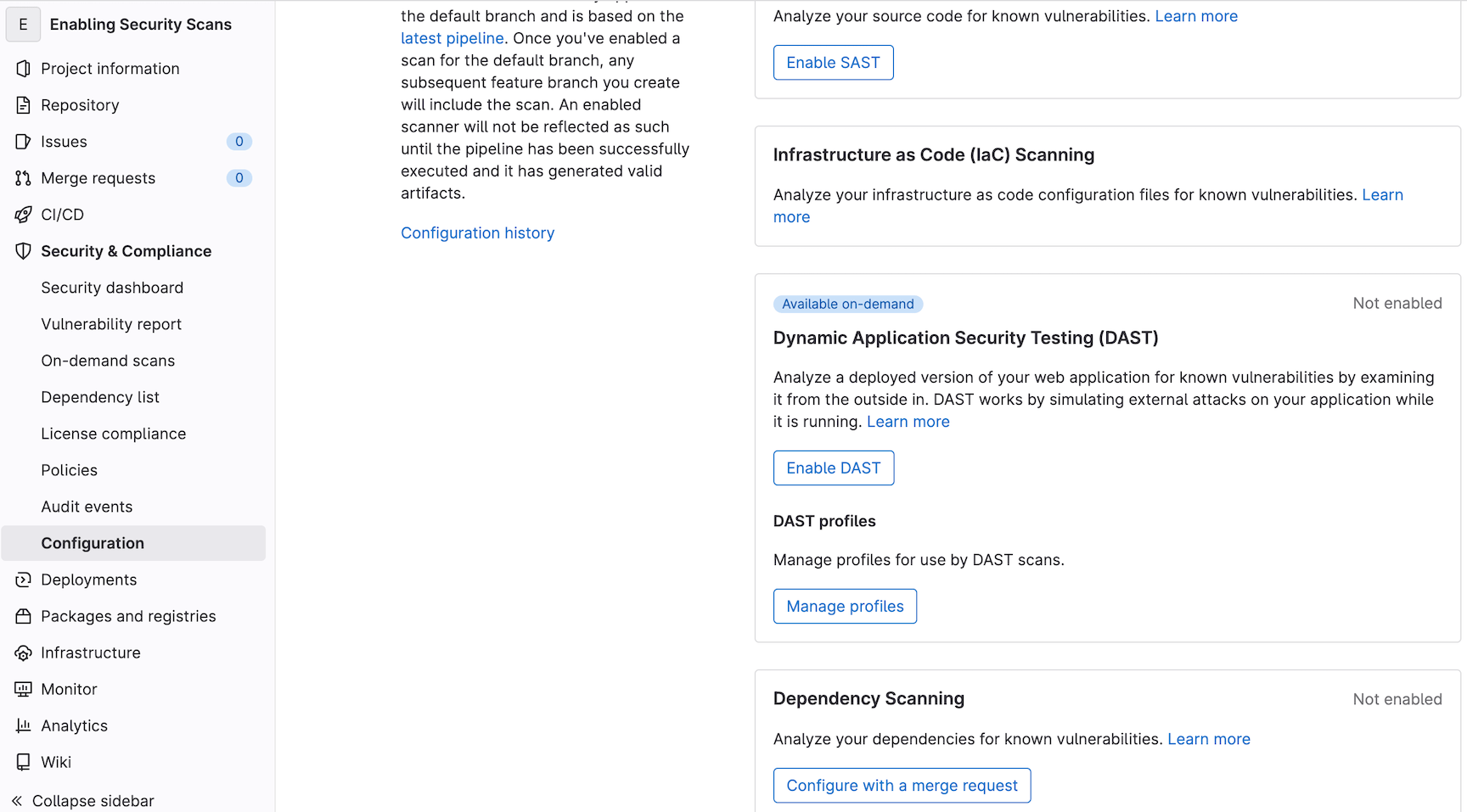
The option to enable dependency scanning is available about halfway down the page. When I click Configure with a merge request, a branch is created and
I am prompted to create a corresponding draft merge request. I'll click Create Merge Request to save the merge request.
Once the merge request has been created, I see that a new branch set-dependency-scanning-config-1 has been created and the .gitlab-ci.yml file has been updated with this code:
# You can override the included template(s) by including variable overrides
# SAST customization:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/application_security/sast/#customizing-the-sast-settings
# Secret Detection customization:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/application_security/secret_detection/#customizing-settings
# Dependency Scanning customization:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/application_security/dependency_scanning/#customizing-the-dependency-scanning-settings
# Container Scanning customization:
https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/application_security/container_scanning/#customizing-the-container-scanning-settings
# Note that environment variables can be set in several places
# See https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/ci/variables/#cicd-variable-precedence
image: alpine:latest
include:
- template: Jobs/Build.gitlab-ci.yml
- template: Security/Dependency-Scanning.gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- build
- test
The change kicks off a pipeline, which will now include the dependency scan.
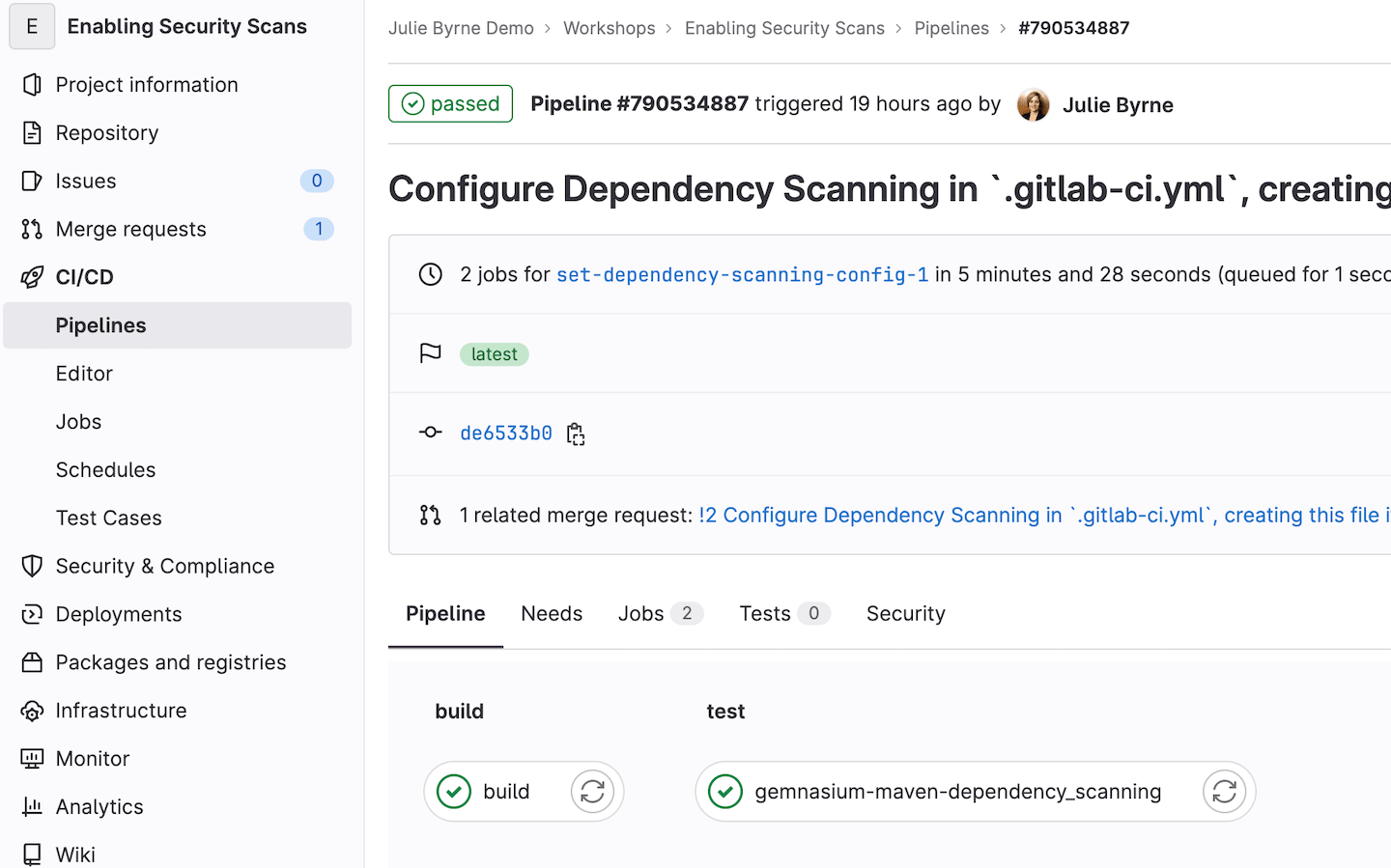
View results of the security scan
For all license tiers, you can view the results of any security scan jobs in the appropriate JSON report that can be downloaded from the merge request.
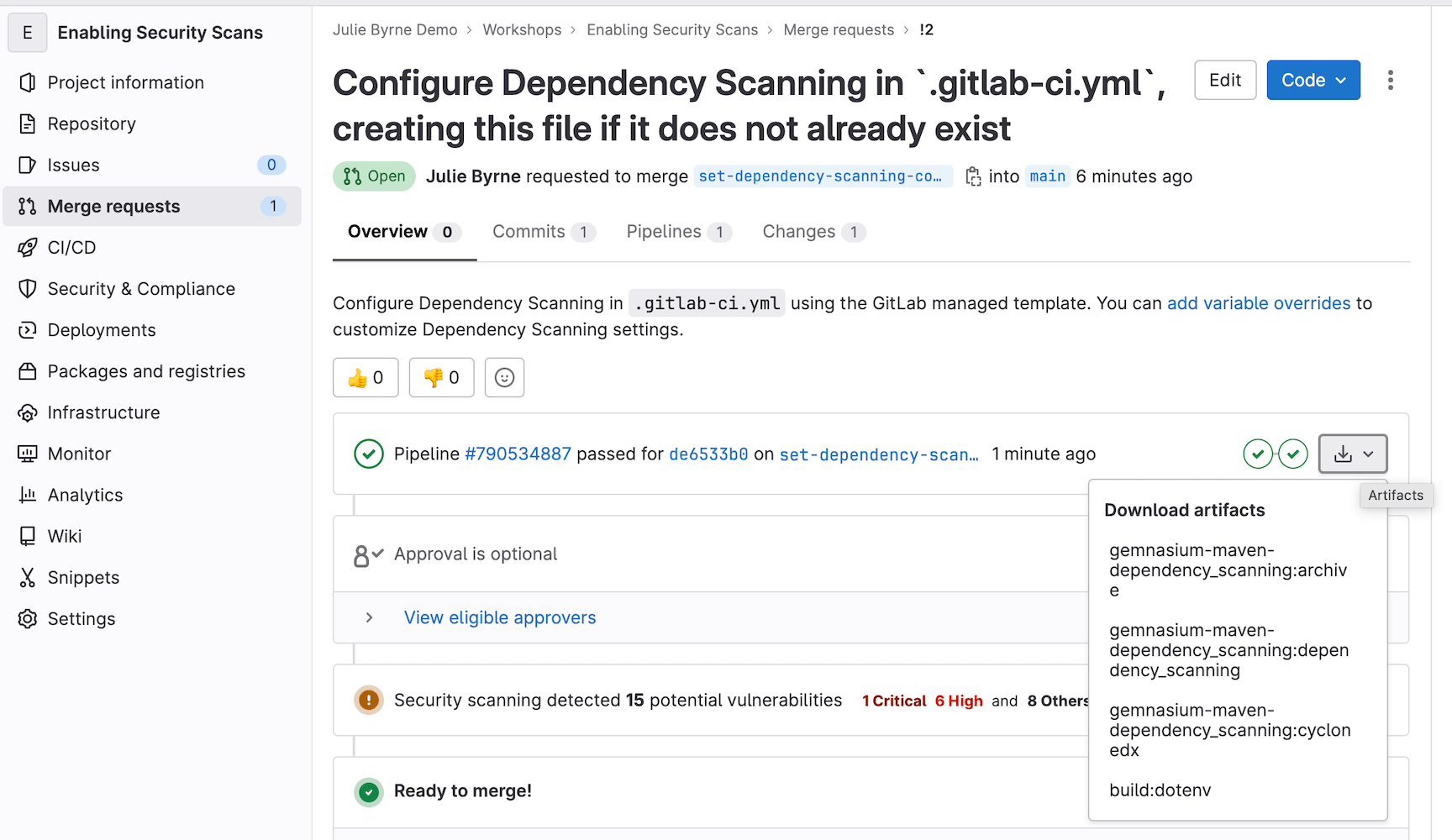
With GitLab Ultimate, you will also see the vulnerabilities found by the scan in the merge request widget.
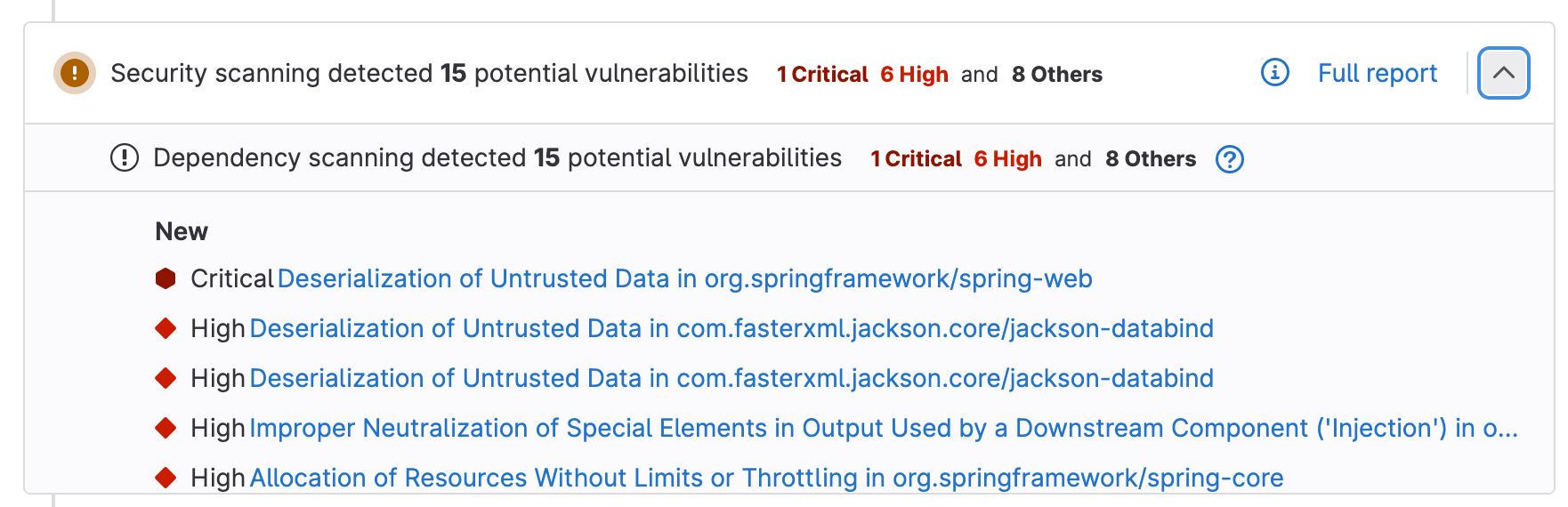
At this point, the .gitlab-ci.yml changes that enable security scanning are only available in the set-dependency-scanning-config-1 branch. I will merge them to main so that the changes will be included in all future feature branches.
With GitLab Ultimate, merging to main will also provide the baseline
Vulnerability Report for our application.
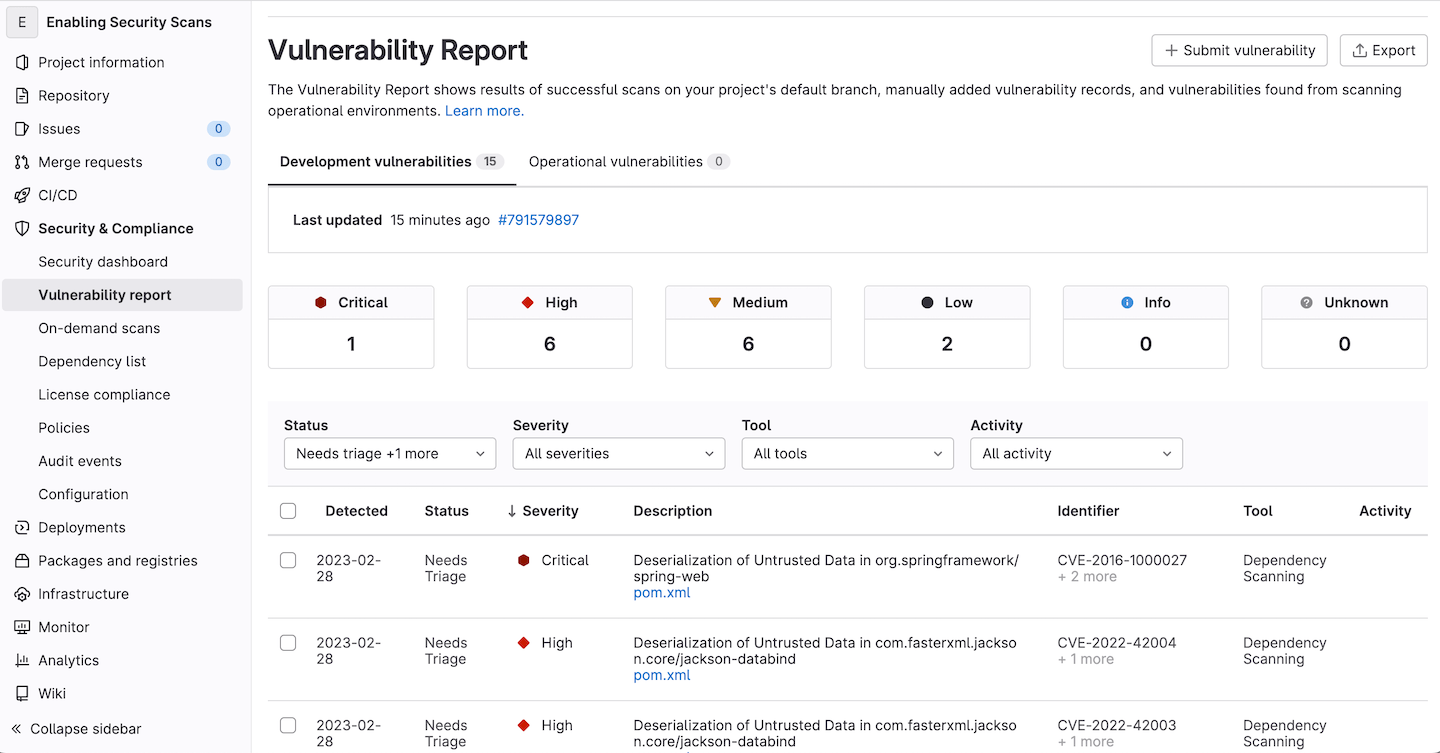
Now, scan results presented in the merge request widget for any new merge requests will only show vulnerabilities introduced by those new code changes in the corresponding feature branch, and not the baseline of vulnerabilities that already exist on main.
Scan enforcement
Once you have enabled your first scans in your CI/CD pipelines, you might be curious to know how you can enforce security scans, or enforce a review and approval when critical vulnerabilities are found in new code changes. I recommend reviewing these resources that cover these topics.
- For Ultimate customers: How to ensure separation of duties and enforce compliance with GitLab
- For Premium customers: How to action security vulnerabilities in GitLab Premium
Now that you've gained comfort with security scanners as part of the GitLab CI/CD pipeline, check out our Getting Started with GitLab Application Security documentation for recommended next steps.
More resources
We want to hear from you
Enjoyed reading this blog post or have questions or feedback? Share your thoughts by creating a new topic in the GitLab community forum.
Share your feedback

